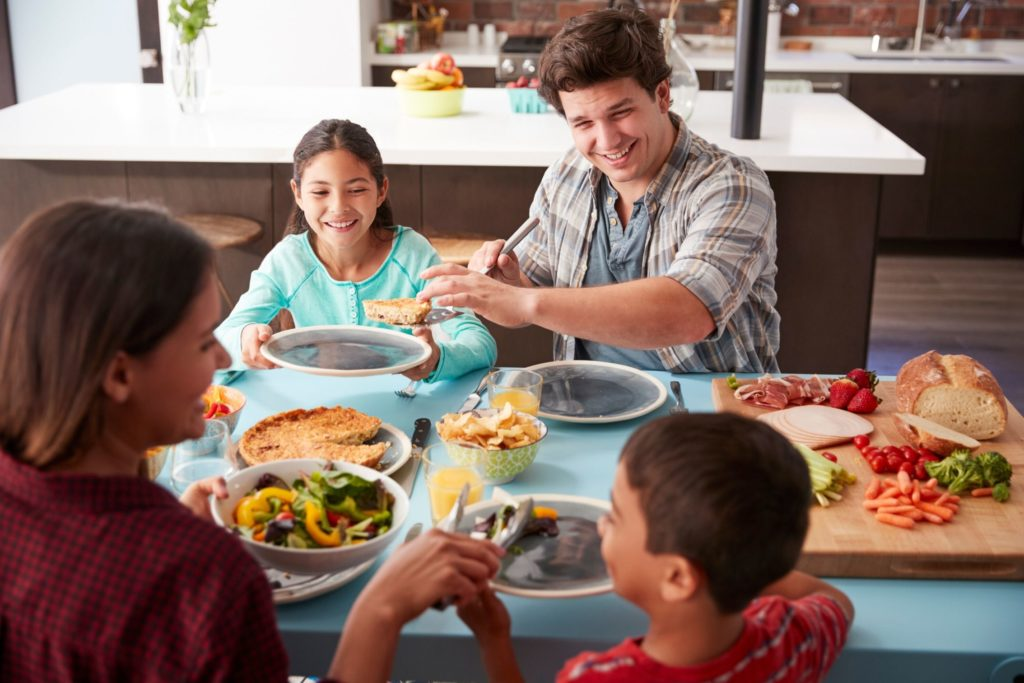
Shared meals and happiness are deeply intertwined experiences that resonate across cultures and generations. The act of dining with others fosters not only nourishment but also a profound social connection that enhances well-being, making it a key happiness indicator. Research increasingly shows that people who engage in shared dining tend to report higher life satisfaction and more positive emotions. In fact, the joy of enjoying meals together may even rival traditional measures of happiness such as income or employment status. As societal trends indicate a shift towards solitary dining, the importance of cultivating shared meals becomes increasingly vital to maintaining our collective happiness.
When we discuss communal meals and joy, we tap into an essential aspect of human experience. Engaging in the practice of eating together is a powerful social ritual that nurtures relationships and fosters emotional well-being. Many individuals may overlook the significance of these interactions, yet studies reveal that communal dining can significantly impact our happiness levels. This phenomenon highlights the importance of social connections in promoting a fulfilling life and suggests that investing time in shared meals can be a simple yet effective strategy for enhancing one’s overall happiness. Understanding the nuances of this relationship can pave the way for more meaningful connections and improved mental health.
The Connection Between Shared Meals and Happiness
Dining with others plays a crucial role in enhancing well-being, with extensive research highlighting that the practice can serve as a vital happiness indicator. When individuals regularly engage in shared meals, they not only cultivate deeper social connections but also foster a sense of belonging and community. This aligns with various happiness indicators, which often emphasize the importance of social support structures in promoting emotional wellness. Enjoying a meal together facilitates meaningful conversations and helps build memories, which are pivotal for personal happiness.
Moreover, the impact of shared dining goes beyond the mere act of eating. It serves as an opportunity for individuals to bolster their emotional health by experiencing joy and laughter in the company of loved ones. The correlation identified in studies, where frequent shared meals translate to increased satisfaction in life, indicates the significant role these interactions play in shaping positive feelings. As society becomes more fragmented, it’s essential to recognize how shared meals might bridge that gap and cultivate lasting joy in our lives.
Dining Alone: A Growing Trend and Its Implications
Recent statistics from the American Time Use Survey reveal a concerning trend—more Americans are dining alone than ever before. With approximately 25% of people reporting solitary meals, this increase over the past two decades highlights a shift towards isolation, particularly among younger demographics. The decline in shared dining experiences is alarming, as it appears to negatively correlate with overall happiness and mental well-being. Individuals who frequently dine alone may miss out on the emotional benefits derived from social interactions, emphasizing the importance of fostering a culture that values togetherness.
The implications of this trend are far-reaching, potentially impacting mental health and community cohesion. As social isolation rises, so too does the urgency to address the decline of shared meals within our society. Encouraging communal dining experiences could serve as a remedy for the loneliness epidemic, allowing individuals to reconnect with others. Policymakers could explore initiatives that promote social dining settings, whether through community events or local dining campaigns, aiming to reignite the tradition of shared meals—essential for nurturing happiness and emotional richness.
Strategies to Foster Shared Dining Experiences
To combat the isolation brought on by a growing culture of dining alone, several actionable strategies can be implemented to encourage shared meals. For instance, community-based initiatives that promote potluck dinners or shared cooking classes can create opportunities for individuals to connect and bond over food. These environments not only enhance social connections but also serve as platforms for cultural exchange, enriching the dining experience with diversity and shared stories. Encouraging neighborhoods to host regular meal-sharing events could foster friendships and create a robust support network.
Additionally, organizations can develop programs aimed at reintroducing shared dining into daily routines. For instance, workplaces could offer lunch programs that encourage employees to dine together, enhancing team cohesion and overall job satisfaction. Schools could implement family-style lunch settings, enabling students to learn the value of sharing meals at an early age. By creating more opportunities for communal dining, we can establish a robust social fabric that significantly contributes to individual and collective happiness.
Happiness Indicators: The Role of Shared Meals
Diving into happiness indicators, research suggests that shared meals can be just as critical as traditional metrics like income when evaluating overall life satisfaction. The straightforward nature of measuring shared dining frequencies—simply asking if one dined with others in a given timeframe—offers a novel approach to gauging well-being. By focusing on experiences rather than financial status, we can gain deeper insights into the factors influencing happiness. Recognizing shared meals as a significant happiness indicator provides a fresh perspective on social well-being.
Additionally, this shift towards viewing shared meals as essential to well-being aligns with a broader understanding of social connection’s importance. Individuals with robust social ties often report higher levels of happiness, reflecting how shared dining experiences serve as a fundamental part of maintaining these connections. By integrating this understanding into policies and community programs, we can promote environments that nurture social interactions and prioritize shared experiences, ultimately enhancing happiness and collective well-being.
The Psychological Benefits of Dining with Others
The psychological benefits of dining with others speak volumes about the intricate relationship between food, company, and mental health. When people share meals, the communal aspects invoke feelings of comfort, support, and inclusion. These experiences can alleviate feelings of loneliness and anxiety, creating a safe space for individuals to express themselves and connect with others. Understanding these psychological dynamics underlines the necessity to encourage shared dining as a means of fostering emotional health and resilience in communities.
Research also suggests that the act of sharing meals can lead to a reduction in stress levels. Engaging in conversation and laughter around the dining table stimulates the release of oxytocin, often referred to as the ‘bonding hormone’, which helps individuals feel more connected and less isolated. This biological response reinforces the idea that shared meals are not just a culinary experience but a significant contributor to mental wellness, acting as a buffer against the stresses of modern life.
Building Stronger Communities Through Shared Dining
Shared meals are more than just personal happiness boosters; they also have the potential to strengthen communities. When individuals engage in communal dining experiences, they foster bonds with their neighbors, creating a sense of belonging and mutual support. By turning to shared dining practices, communities can bridge cultural divides, allowing people to learn from one another and build empathy through the exploration of diverse culinary traditions. This engagement can significantly enhance community cohesion, creating a network of support that can positively impact overall well-being.
Furthermore, communal meals can serve as a vehicle for social change, providing a platform for discussions that address community issues. Local leaders can harness the power of shared dining to promote initiatives that tackle social isolation, food insecurity, and community engagement. By designing events that bring people together over food, communities can create lasting impacts, making shared meals an essential element in the quest for societal happiness and well-being.
Cultural Perspectives on Shared Meals and Happiness
Cultural perspectives on shared meals emphasize the universal significance of dining together. In many cultures, communal dining is a cherished tradition that reinforces societal bonds and values. For instance, in Mediterranean cultures, sharing meals with family and friends is seen as essential for nurturing relationships and cultivating joy. Studying these cultural norms can offer insights into how dining practices across the globe influence happiness and well-being, highlighting the importance of connection through food.
Understanding the cultural dimensions of shared meals allows for the appreciation of different practices that foster happiness. For example, in some Asian cultures, family gatherings centered around food emphasize respect and togetherness, creating a strong sense of community. By exploring these varied traditions, one can gain a broader appreciation for how shared dining transcends mere sustenance, transforming meals into vital experiences of joy, healing, and connection that contribute significantly to overall happiness.
Future Research on Shared Meals as a Well-being Indicator
Future research is vital to dissecting the nuances of shared meals as an indicator of well-being and happiness. Investigating the causal relationships between dining with others and increased satisfaction can deepen our understanding of social behaviors and their impact on mental health. As researchers like Micah Kaats pave the way for further inquiries, it becomes crucial to formulate hypotheses based on diverse populations and cultural contexts. Such explorations may reveal how shared meals operate as a universal language of connection, vital for emotional health across different societal frameworks.
Moreover, integrating quantitative and qualitative methodologies could provide a more holistic view of how shared meals impact happiness. By pairing surveys with personal narratives or observational studies, we can enrich the current understanding of shared dining’s emotional, psychological, and sociocultural dimensions. As the interest in social well-being grows, prioritizing research in this area may ultimately lead to actionable insights that can inform policies aimed at enhancing community engagement and public health through the power of shared meals.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do shared meals contribute to happiness?
Shared meals help enhance happiness by fostering social connections and creating a sense of community. Research indicates that individuals who dine with others tend to report higher levels of life satisfaction, as sharing meals exposes them to positive interactions and emotional exchanges.
Is dining with others a key indicator of well-being?
Yes, dining with others is considered a crucial happiness indicator. Studies show that the number of shared meals directly correlates with well-being, illustrating that people who enjoy more communal dining experiences often experience greater joy and fulfillment in their lives.
What are the benefits of social connections formed through shared dining?
Social connections formed through shared dining provide emotional support, reduce feelings of loneliness, and increase feelings of belonging, all of which are vital for maintaining a positive state of well-being and enhancing overall happiness.
Can increased shared meals lead to improved mental health?
Absolutely, increasing the frequency of shared meals can lead to improved mental health. Engaging in communal dining experiences can promote happiness, lessen feelings of isolation, and contribute to a more fulfilling life, especially in times of social disconnection.
Why is it important to encourage more shared meals in communities?
Encouraging more shared meals is vital because it can combat social isolation and enhance community cohesion. By facilitating shared dining opportunities, we can potentially increase overall happiness levels within communities and improve individual well-being.
What role do cultural practices around shared meals play in happiness?
Cultural practices surrounding shared meals often create significant opportunities for social bonding and celebration. These traditions can enhance happiness by providing individuals with a sense of identity and belonging, deeply enriching their emotional and social lives.
How does modern society impact our ability to share meals?
Modern society’s increasing trend toward dining alone can negatively impact our ability to share meals and form social connections. Addressing this issue may involve community initiatives aimed at promoting shared dining experiences to enhance collective happiness.
What future research is needed regarding shared meals and happiness?
Future research should explore the causal relationship between shared meals and happiness. Specifically, studies could investigate whether people become happier as they share more meals or if happier people are simply more inclined to invite others to dine.
How can policymakers use shared meals as a strategy for enhancing well-being?
Policymakers can use shared meals as a strategic tool for enhancing well-being by creating initiatives that encourage community dining events, support food-related projects, and promote social engagement, ultimately aiming to improve mental health and happiness outcomes.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Shared meals are a strong indicator of happiness, potentially more reliable than income or employment status. |
| People who eat meals together report higher life satisfaction and positive emotions. |
| Increased solitary dining habits observed, with 1 in 4 Americans reporting eating alone recently. |
| The trend of dining alone is particularly severe among younger generations. |
| Correlation between shared meals and happiness is significant but does not clarify causation. |
| Future research is needed to explore how meal sharing can enhance happiness. |
| Tracking shared meals might be a simpler and more effective measure of well-being. |
| Encouraging social dining can be an important policy intervention for improving mental health. |
Summary
Shared meals and happiness are closely linked, as recent studies suggest that dining with others positively impacts well-being. A significant body of research indicates that individuals who share meals often experience higher life satisfaction and express more positive emotions than those who dine alone. This burgeoning understanding highlights the importance of social connections in our daily lives. In a world where increasing numbers of people are eating alone, especially among younger generations, fostering opportunities for shared meals may serve as an essential strategy for boosting happiness and enhancing mental health.